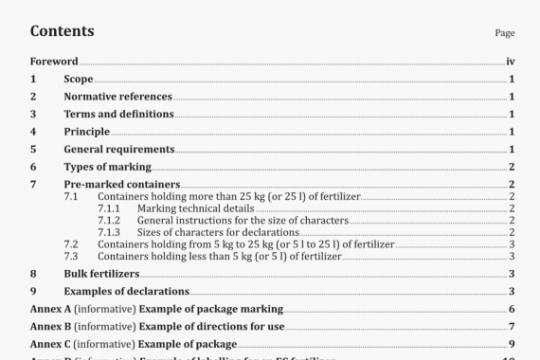
ISO 15142-1:2003 pdf download
ISO 15142-1:2003 pdf download.lmplants for surgery – Metal intramedullary nailing systems -Part 1: lntramedullary nails.
3.2.2
un-united bundle nail
nail intended for use in parallel groups so that more than one nail is usually inserted in the intramedullary cavity
NOTE The individual nails are not joined to each other but may be in contact.
3.3
cannulated nail
intramedullary nail that has a hole along the longitudinal axis over its full length
NOTE The inner or outer contour of a hollow nail, or both contours, can be circular, polygonal, cloverleaf, star-shaped, etc.
3.4
closed-section nail
cannulated nail whose cross-sections perpendicular to the nail’s longitudinal axis have no discontinuities along the outer wall, other than for connection elements to accommodate locking components or insertion/removal devices
3.5
connection element
integral part of the nail intended to connect the nail to a locking component or insertion/removal device
EXAMPLE Hole, window, bore, slot (see Figure 5) or thread.
3.6
cross-arm
auxiliary component which is used for fixation into the femoral head or metaphysis and is intended to provide additional stability across a fracture
3.7
cross-arm intramedullary nail
intramedullary nail whose function is dependent on the use of a cross-arm
3.8
curved nail
nail whose longitudinal axis is curved over at least a part of its length
3.9 Diameters
3.9.1
inner diameter
diameter of the largest circle which is enveloped by the contour of the cross-section of a hollow nail
See Figure 4.
NOTE The site of measurement is indicated if the nail is not of uniform diameter throughout its length.
3.9.2
minimum inner diameter
maximum possible diameter of a guidewire of circular diameter over which the nail, which may be of variable diameter, can be passed
3.9.3
outer diameter
diameter of the smallest circle that will envelop the outer cross-section of the nail
See Figure 4.
NOTE The site of measurement is indicated if the nail is not of uniform diameter throucihout its length.
3.10
insertionlremoval device
device external to the nail which connects temporarily to the nail through the nail’s connection element(s) in order to assist the insertion and/or removal of the nail
EXAMPLE Driving handle, drill guide, extractor bolt or hook.
3.11 Lengths
3.11.1
effective length
length of the nail as measured by the shortest distance between the two ends
3.11.2
overall length
length of the nail as measured along the centreline of the nail from end to end
3.12
lockable intramedullary nail
intramedullary nail that has provisions for the application of locking elements to improve temporary fixation in bone
See Figures 1, 2 and 3.
NOTE These auxiliary components are not always used.
3.13
locking component
device or component which controls or minimizes relative motion between the intramedullary nail and bone and which is designed to fit into the connection elements of the appropriate nail
EXAMPLE Screw, blade, bolt or cross-arm.
3.14
multiple component nail system
nail system which consists of more than one major temporary fixation component, such as a cross-arm configurations or bundle nails
3.15
open-section nail
cannulated nail whose cross-sections perpendicular to the nail’s longitudinal axis have one or more discontinuities along the outer wall
3.16
single-component nail system
nail system that consists of one major temporary fixation component, except for locking components such as bolts/screws
3.17
solid nail
nail with a solid cross-section over its entire length except for connection elements
NOTE The contour can be circular, polygonal, cloverleaf, star-shaped, etc.
3.18
straight nail
nail whose longitudinal axis is straight over its length.
4Materials
The metallic materials used for an intramedullary nail shall be chosen in accordance with ISO 14602 and theappropriate part of lSO 5832.
5 Surface requirements
The surface finish shall not adversely affect the biocompatibility of the metal used. The effect of surface finishon biocompatibility shall be considered in the risk analysis for the device (see ISO 14602).
NOTE The surface finish of the implant is normally selected so that it will not encourage surface bone ongrowthwhich might make removal of the implant difficult or impossible.
6 Marking
The implant shall be marked on its surface in accordance with IlSO 14630. In the case of anatomical shapingor orientation (left or right) of the device, there shall be a unique marking to avoid wrong positioning.
7 Product label
The package shall be labelled in accordance with ISO 14630. The label shall include,as a minimumnail-specific information such as length and diameter.