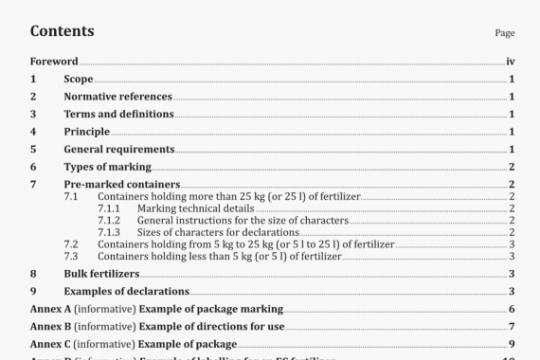
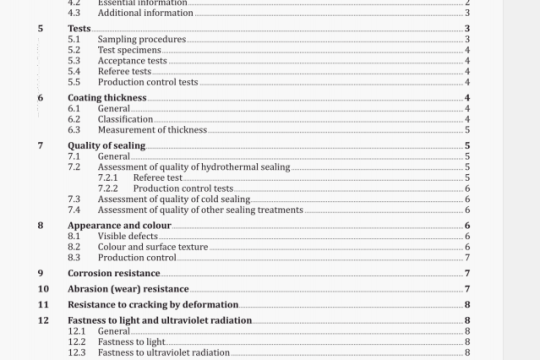
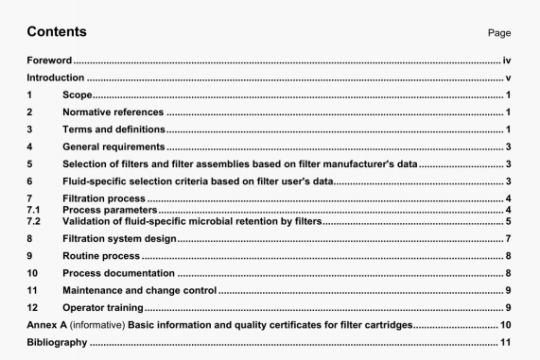
ISO 14817:2002 pdf download
ISO 14817:2002 pdf download.Transport information and control
systems-Requirements for an ITS/TICscentral Data Registry and ITS/TICS Data Dictionaries.
Data Registry
DR
store of data, characterized in a consistent manner, as determined according to the provisions of this
International Standard, used for a specific purpose (in this case ITS/TICS)
NOTE The data registration process provides a determination of the ITS Data Dictionary items accepted into the ITS/TICS Data Registry. The Data Registry contains not only data about data concepts in terms of their names and representational forms but also substantial data about the semantics or meaning associated with the data concepts. A Data Registry may contain data that assists information interchange and reuse, both from the perspective of human users and for machine-interpretation of data concepts. The Data Registry is comprised of items only from ITS/TICS Data Dictionaries, showing their source; however, not all ITS/TICS Data Dictionary items shall necessarily be submitted for inclusion, or accepted, into the Data Registry.
4.12
data registrar
organizational element or an individual appointed by lSO/TC 204 to undertake the day-to-day management of the Data Registry process
4.13
data registration process
process by which data is formally described and provided to an approved location in the Data Registry
NOTE This process is effected under the control of the ITS/TICS data registrar, in accordance with the requirements of this International Standard.
4.14
data type
classification of the collection of letters, digits, and/or symbols used to encode values of a data element based upon the operations that can be performed on the data element
4.15
identifier
means of designating or referring to a specific data concept instance
4.16
generalization
specialization/generalization relationship in which an object class of a specialized element (child) is substituted for a generalized element (parent)
4.17
information model
graphical representation that logically organizes various data concepts by depicting key relationships among the data concepts
EXAMPLE An information model might specify that a Vehicle may be described by a variety of properties, such as:
Make, Model, Year, and Vehicle Identification Number. Likewise a Collision might be described by properties such as
Time of Occurrence, Severity, and Number of Vehicles Involved. Finally, the model might depict that a Collision has a
many-to-many relationship to a Vehicle.
NOTE 1 Within the scope of this International Standard, information models are depicted using UML Class Diagrams.
NOTE 2 This International Standard uses the term information model in order to reflect the fact that relationships give the data a context and thereby transforms data into information. Some groups use the term data model. See also data model.
4.18
interface dialogue
data concept; collection of all the temporal sequences of messages, including variants such as multiple responses, that are used to accomplish the services that the interface dialogue provides
4.19
message
data concept; grouping of data elements and/or data frames, as well as associated message metadata, that is used to convey a complete unit of information
NOTE For the purposes of this International Standard, a message is an abstract description; it is not a specific instance.
4.21
meta
word denoting a description that is one level of abstraction above the concept being described
4.22
meta attribute
any documenting characteristic of a data concept
4.23
metadata
data that defines and describes other data
4.24
name
indexical term used by humans as a means of identifying data eiements and other data concepts
4.25
object class
data concept; construct used to represent any kind of object (also referred to as an entity) within a ITSITICS information environment
4.26
property
data concept; documenting characteristic of an object class used to group and differentiate individual objects
4.27
semantics
meaning, including concept(s), associated with a given data concept
4.28
syntax
structure of expressions in a language and the rules governing the structure of a language
4.29
value domain
data concept; expression of a specific and explicit representation of some information about something of interest within the ITS/TICS domain
5 Symbols and abbreviated terms.