ISO 15682:2000 pdf download
ISO 15682:2000 pdf download.Water quality – Determination of chlorideby flow analysis (CFA and FlA) and photometric or potentiometric detection.
3.4.2.7 Registration unit (e. g. strip chart recorder, integrator or printer/plotter).
In general peak height signals are evaluated.
3.4.2.8 Autosampler, if required.
NOTE In Figures B.3 and B.4, continuous flow systems with internal diameters of 2 mm (“macroflow”) are described. Similar systems with an internal diameter of 1 mm (“microflow”) are also allowable.
3.4.3 Additional apparatus
3.4.3.1 Graduated flasks, nominal capacity 100 ml, 200 ml and 1 000 ml.
3.4.3.2 Graduated pipettes, nominal capacity 1 mlto 100 ml.
3.5 Sampling and sample pretreatment
Store the samples in either glass or plastic containers for up to one month. Sample preservation is not required
(see ISO 5667-3).
3.6 Procedure
3.6.1 Preparation of the measurement
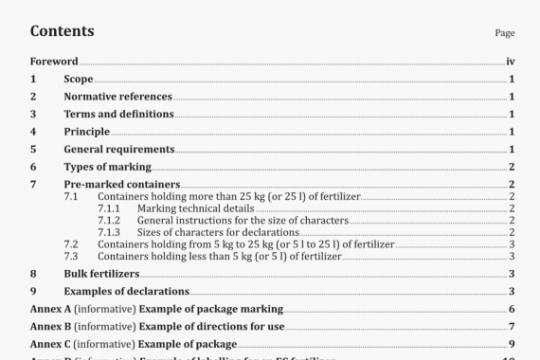
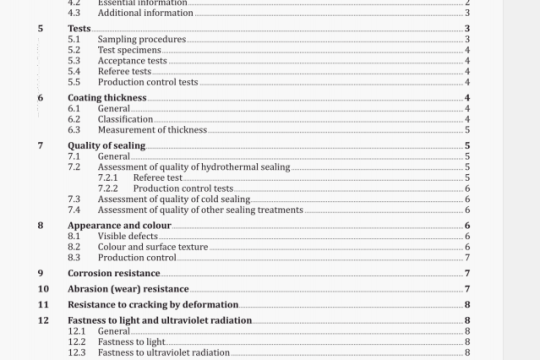
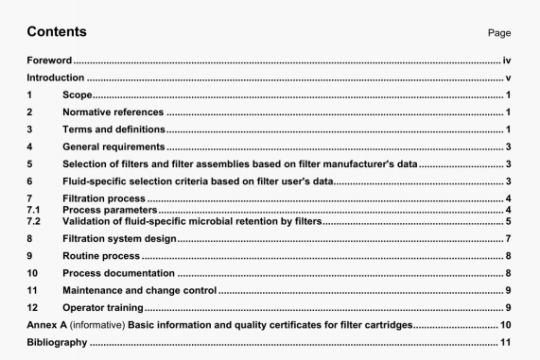
a) Assemble the flow analysis system (FIA or CFA) in accordance with the flow diagrams (3.4.11 3.4.2; Figures
B.1 to B.4).
b) Before analysis, insert the tubes of the carrier solutions Cl to C3 (3.3.12, 3.3.13) and the reagent solution (3.3.9) into the appropriate canisters. Run the system for 10 mm. Wait for a stable baseline and adjust the baseline to zero.
C) When the baseline shows no more drift, the system is ready for analysis. Check the reagent blank in accordance with 3.6.3 and calibrate in accordance with 3.6.4.
3.6.2 Quality requirements for the measuring system
3.6.2.1 Instrument performance check
The absorbance per centimetre of optical pathlength measured for the calibration solutions 3.3.14) shall be in the range from 0,03 to 2,0.
NOTE If the photometric detector does not give any absorbance readings, the absorbance may then be determined by comparison with an external absorbance-measuring spectrometer.
3.6.2.2 Daily sensitivity adjustment
If a recorder for the calculation of results is used, transfer the sample probe into a chloride calibration solution (3.3.14) with the highest concentration of the selected working range (10 mg/I, 100 mg/I or 1 000 mg/I, respectively). When there is a positive response at the registration unit due to the colour produced from the calibration solution, adjust the response to read about 95 % of full-scale deflection.
3.6.3 Checking the reagent blank
The reagent solution (3.3.9) shall not exceed an absorbance per centimetre of optical path length of 0,3. Otherwise consider the water as contaminated with chloride and take alternative steps. The absorbance can be measured by an external spectrometer.
4.3.6.2 FIA ISA solution for samples with interfering ions (4.2) in the range (1 mg/I to 1 000 mg/I CI)
In a 1 000 ml volumetric flask dissolve 7,2 g of potassium bromate (4.3.3) and 38 ml of nitric acid 11(4.3.4) in approximately 800 ml of water. Make up to volume with water.
This solution shall be prepared fresh daily.
4.3.7 Ionic strength adjustment buffer (ISA) solution for CFA (P2 in Figure B.6) for all ranges (1 mg/I to
1 000 mg/I chloride).
4.3.7.1 CFA ISA for samples without interfering ions (4.2)
In a 1 000 ml volumetric flask dissolve 3 ml of nitric acid 11(4.34) and 50,5 g of potassium nitrate (4.3.2) in approximately 900 ml of water, add 1 ml of detergent solution (3.3.8) and fill to the mark with water.
This solution may be stored for one month.
4.3.7.2 CFA ISA for samples with interfering ions (4.2)
In a 1 000 ml volumetric flask dissolve 38 ml of nitric acid 11(4.3.4), and 7,2 g of potassium bromate (4.3.3) in approximately 900 ml of water, add 1 ml of detergent solution (3.3.8) and make up to volume with water.
This solution shall be prepared fresh daily.
4.4 Apparatus
4.4.1 Flow analysis system (FIA and CFA)
The flow injection system or the continuous flow system, respectively, consists of the components outlined in 3.4.1 or 3.4.2. (See Figures B.5 and B.6, and also Note in 3.4.2.8).
Instead of a photometer, a specific chloride-ion-selective electrode with a reference electrode and a millivoltameter with high impedance inlet (> 1 MQ) are required.
4.4.2 Additional apparatus
The requirements given in 3.4.3 apply.
4.5 Sampling
The requirements given in 3.5 apply.
4.6 Procedure
4.6.1 Preparation of the measurement
Before starting the analysis, stabilize the baseline by pumping the required solutions (4.3.5, 4.3.6, 4.3.7) through the system for approximately 10 mm.
When the baseline shows no more drift, the system is ready for sample analysis.