ISO 6497:2002 pdf download
ISO 6497:2002 pdf download.Animal feeding stuffs -Sampling.
5 Identification and general inspection of the lot prior to sampling
Positively identify the lot in question before any samples are taken, and, for this purpose, compare, as appropriate, the number of items in the lot, the mass of the lot or the volume of the lot, and the markings on containers and labels, with the entries on the relevant documents.
Note for inclusion in the sampling report any features, relevant to the taking of representative samples, concerning the condition of the lot and of the surroundings.
Separate damaged portions of the lot and/or, if the lot is unduly heterogeneous, divide it into portions with more similar properties. Treat each of these portions as separate lots.
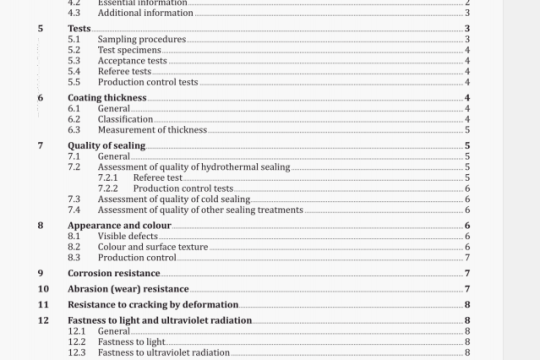
6 Sampling equipment
6.1 General
Select a sampling device appropriate to the particle size of the product, the size of the sample to be taken, the size of the container, the physical state of the product, etc.
6.2 Apparatus for taking increments from solid products
6.2.1 Examples of apparatus for manual sampling
6.2.1.1 Sampling from bulk
Examples are an ordinary shovel, hand-scoop, cylindrical sampler (for example sampling spear, stick-trier or sleeve-trier) and conical sampler. The sampling spear may comprise one or more compartments.
Sampling of products in motion at relatively low flow rates can be performed manually.
6.2.1.2 Sampling from bags or other packages
Examples are a hand-scoop, sack-type sampling spear or trier, cylindrical sampler, conical sampler and riffle
divider.
6.2.2 Examples of apparatus for mechanical sampling
Approved apparatus for taking increments periodically from a flow of product (for example pneumatic apparatus) may be used.
Sampling of products in motion at high flow rates can be performed by machines with manual control.
6.3 Apparatus for taking increments from liquid or semi-liquid products by manual or mechanical means
Examples are a stirrer plunger, agitator, sampling bottle, sampling tube, zone sampler and dipper, of an appropriate size.
6.4 Cleanliness
When taking, reducing, storing and handling samples, special care shall be taken to ensure that the properties of the samples and the sampled lot are not affected. The sampling equipment shall be clean, dry and free from foreign odours. The material from which the sampling apparatus is made shall not influence the quality of the sample. Apparatus shall be cleaned thoroughly between samples. This is particularly important when sampling feed with high oil content. Sampling personnel shall wear disposable gloves and dispose of them between samples so as not to contaminate the subsequent sample.
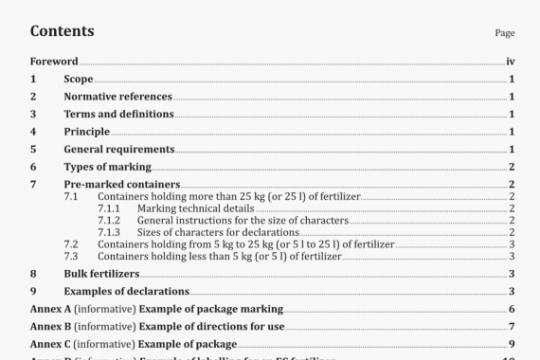
7.1 General requirements
The sample containers shall ensure that the characteristics of the sample are maintained until testing is carried out. They shall be of such size that they are almost completely filled by the sample. They shall be capable of being sealed in such a way that it will not be possible to open and reseal them without this being detected.
7.2 Cleanliness
The sample containers shall be clean, dry and free from foreign odours. The material from which the sample
containers are made shall not influence the quality of the sample.
7.3 Sample containers for solid products
Sample containers for solid products and the lids of such containers shall be made of waterproof and greaseproof material (for example glass, stainless steel, tin or a suitable plastics material), shall be wide-mouthed and preferably cylindrical, and shall be of a capacity appropriate to the size of the sample they are intended to contain. Suitable plastic bags are also acceptable. The containers shall be capable of secure and waterproof closure. If the samples are to be used for the determination of photosensitive substances, like vitamins A, D3, folic acid, B2 and C and slightly sensitive substances, like vitamins K3, B6 and B12, the containers shall be opaque.
7.4 Sample containers for liquid and semi-liquid products
Such containers shall be made of a suitable material (preferably glass or plastics material), of the appropriate capacity, capable of airtight closure and preferably dark-coloured. Note the requirements in 7.3 for samples which are to be used for the determination of photosensitive substances.
8 Procedure
8.1 Sampling location
If possible, sampling shall be carried out at places protected from adventitious contamination such as damp air, dust or soot. If possible, samples shall be taken during loading or unloading. If sampling cannot be carried out whilst the material is in motion, the lot to be sampled shall be so arranged as to make each part accessible, so that representative laboratory samples are obtained.
8.2 Classification of products for the purpose of sampling
For sampling purposes, animal feeding stuffs are classified as follows:
a) solid feeding stuffs — grains, seeds, pulses and pellets;
b) solid feeding stuffs — meals and powders;
c) roughages;
d) licks and blocks;
e) liquid or semi-liquid feeding stuffs.