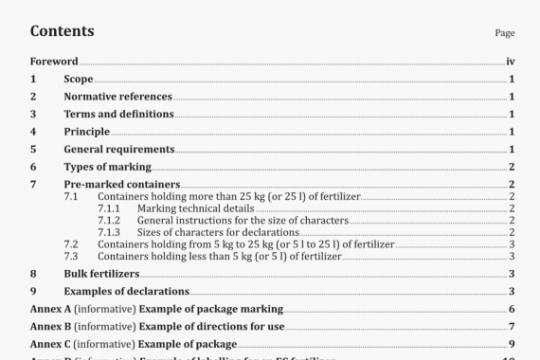
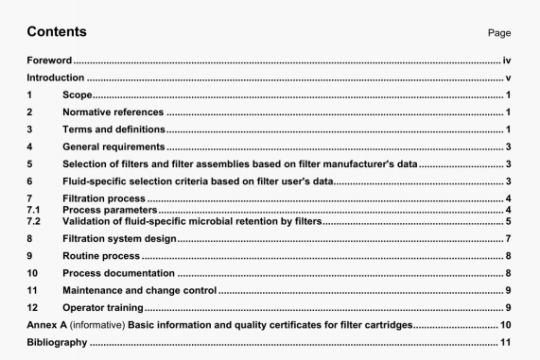
ISO 8442-7:2000 pdf download
ISO 8442-7:2000 pdf download.Materials and articles in contact with
foodstuffs-Cutlery and table holloware 一Part 7: Requirements for table cutlery made ofsilver, other precious metals and theiralloys.
B.2 Reagents
Sodium chloride solution with a mass fraction of 1 % consisting of one part by mass sodium chloride in 99 parts demineralized/distilled water.
During the test, unless otherwise stated, use only reagents of recognised analytical grade and only distilled water or water of equivalent quality.
B.3 Apparatus
A suitable apparatus is shown in figure B.1, and comprises a glass or plastics container and a cover, which may he glass or plastics, and a plastics specimen rack with means to raise and lower this into the container.
NOTE Other methods of specimen support may be used provided that there is a minimal contact of the specimen with the supporting means.
Calibrated microscope or lens of at least 4 times magnification.
B.4 Procedure
B.4J Wash the selected samples thoroughly in hot soapy water. Thoroughly rinse and then degrease the samples in acetone or methylated spirits.
B.4.2 Fill the container with the sodium chloride solution (see B.2) using at least 1 litre of solution for every square decimetre of area of the stainless steel parts of the samples. Bring the container and contents to 60°C ± 2°C. Maintain at this temperature. Do not allow the temperature of the solution to exceed 62 °C at any time, even before the start of the test. Use a fresh sodium chloride solution for each test.
NOTE The temperature of the sodium chloride solution can be conveniently maintained at 60°C ± 2°C by positioning the apparatus in a thermostatically controlled water bath, the level of which is maintained at approximately the same level as that of the sodium chloride solution.
B.4.3 Place the sample in the rack and replace the cover.
B.4.4 Completely immerse and completely withdraw the samples from the solution at the rate of from two to three times per minute for 6 h.
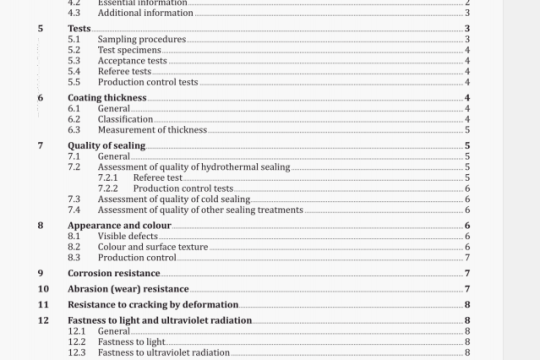
The knife, clamped at the handle and loaded at the blade or prong tip, is raised until the load
is just lifted. The angle of permanent deformation after release of the load is measured.
C.2 Apparatus
Apparatus suitable for carrying out the test as shown in figure C. I.
NOTE The hand lever shown in figure C. I should not he attached before both scales
are set to zero and should he removed before the angle of permanent set is measured; otherwise the hand lever exerts a torque on the pivoted clamp which will result in false measurements of permanent set.
C.3 Procedure
C.3.1 Clamp the handle of the sample to be tested in the pivoted clamp. Position the handle in the clamp so that during the test the tip of the blade, or carving fork prongs, and the end of the handle will remain in essentially the same horizontal plane.
C.3.2 Clamp the blade to the unloaded tip clamp, ensure that the hand lever is removed from the apparatus and then set both scales to zero.
C.3.3 Connect a test load of 30 N ± 1 N to the tip clamp aiid rotate the shaft of the pivoted clamp by means of the hand lever until the tip clamp just rises from the guide rails. Maintain it in this position for 10 s. Return the hand lever to a position of rest and remove the hand lever. Remove the load from the tip clamp and read off the angles of deflection, a and b from the relevant scales. Add these two angles to give the angle of permanent deformation (see figure C.2).
C.3.4 Turn the sample over and repeat the test in the opposite direction.
C.4 Expression of results
Calculate the permanent deformation as the average of the angles of permanent deformation in the two directions.