ISO 9832:2002 pdf download
ISO 9832:2002 pdf download.Animal and vegetable fats and oils –
Determination of residual technical hexane content.
5.1 Technical hexane, with a composition similar to that of hexane used in industrial processing or, if this is not available, n-hexane.
It is recommended that technical hexane be used for the calibration. This reagent usually has an n-hexane content of 50 % (by mass) and consists mainly of C6 isomers but may include C5 and C7 hydrocarbons.
5.2 Internal standard, n-heptane.
If this is not available, cyclohexane may be used, provided that the solvent (5.1) used for the extraction or
calibration has a negligible content of cyclohexane and/or n-heptane or components with similar retention times.
5.3 Carrier gas, e.g. hydrogen, nitrogen or helium, etc., thoroughly dried and with an oxygen content of less
than 10 mg/kg.
5.4 Auxiliary gases, hydrogen (99,9 % pure, free from organic impurities) and air (free from organic impurities).
5.5 Calibration fat, freshly refined and deodorized vegetable fat, the technical hexane content of which is negligible.
This material should be free from peroxides or other components likely to decompose with the formation of volatile material which could be confused with hydrocarbons during the test.
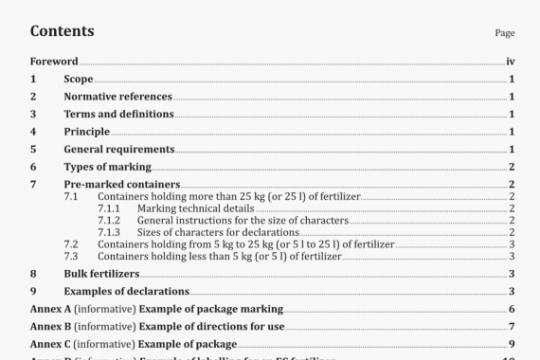
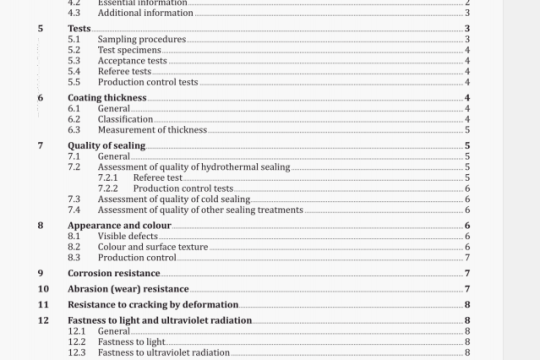
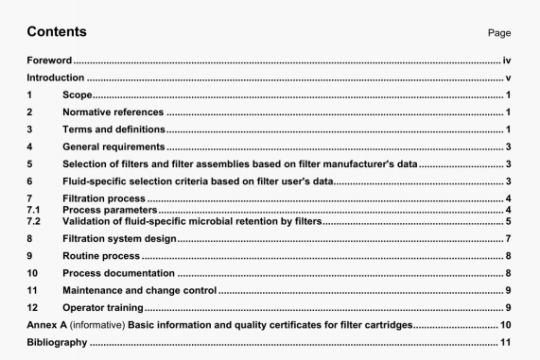
6 Apparatus
Usual laboratory equipment and, in particular, the following.
6.1 Septum vials, of 20 ml capacity.
6.2 Septa, inert to fats and solvents, made of a material such as butyl rubber or red rubber free from hydrocarbon solvent residues and of a suitable quality that they will not swell under the conditions of use, aluminium caps suitable for use with the vials (6.1) and crimping pliers.
6.3 Tongs, suitable for holding the vials (6.1).
6.4 Syringes, of 10 p1 capacity, used only for the analysis of residual technical hexane. They shall not be
cleaned with hydrocarbon solvent.
6.5 Syringes, of 1 p1 capacity, used only for the analysis of residual technical hexane. They shall not be cleaned
with hydrocarbon solvent.
6.6 Syringes, of 1 000 p1 capacity, gas-tight, used only for the analysis of residual technical hexane. They shall
not be cleaned with hydrocarbon solvent.
6.7 Gas chromatograph, with a flame ionization detector and an integrator and/or recorder, equipped with
either
a) a packed glass column, 2 m to 4 m long and of internal diameter 3,2 mm approximately, packed with an acidwashed and silanized diatomaceous earth support of particle size 150 pm to 180 pm (Chromosorb P NAW 60-80 mesh1) is suitable), and coated with 10 % squalane or any other phase permitting the chromatographic separation required, or
b) a glass capillary column, approximately 30 m long and of 0,3 mm internal diameter, coated with methylpolysiloxane of film thickness 0,2 pm.
The injector and detector temperature shall be set at 100 °C and the oven temperature at 50 °C. If a capillary column [see b)] is used, the apparatus shall have a 1/100 split injection system.
NOTE For analyses in series, a headspace gas chromatograph with automatic sample injection and tempering bath has been shown to be satisfactory. In this case, manual injection is not necessary.
6.8 Heating bath, equipped with clamps for holding septum vials, regulated thermostatically at 80 °C ± 2 °C. NOTE For continuous operation, glycerol is recommended as the heating medium.
6.9 Shaking machine
7 Sampling
It is important that the laboratory receive a sample which is truly representative and has not been damaged or changed during transport and storage.
Sampling is not part of the method specified in this International Standard. A recommended sampling method is given in ISO 5555.
It is essential that the sample be protected from gain or loss of solvent residues.
8 Preparation of test sample
Prepare the test sample in accordance with ISO 661, taking care to prevent gain or loss of solvent.
9 Procedure
9.1 Calibration
9.1.1 Weigh, to the nearest 0,01 g, 5 g of calibration fat (5.5) into each of seven vials (6.1). Close each vial with a septum and a cap (6.2).
To six of the seven vials (6.1) add, using a syringe (6.4 or 6.5), the quantity of solvent (5.1) specified in Table ito obtain the concentrations indicated. Do not add solvent to the seventh vial.
Shake vigorously, in the shaking machine (6.9) for 1 h at room temperature, the six vials to which solvent was added.
9.1.2 At the end of this time add, by means of a syringe (6.4), 5 p1 ± 0,1 p1 of internal standard (5.2) to each of the seven vials through the septum.
For hexane contents between 10 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg, it is preferable to add 2 p1 of internal standard (5.2).
Mix the contents vigorously by hand for about 1 mm by moving the vial with a circular motion in a horizontal plane in such a way that the fat does not touch the septum. If this happens, reject the vial and start again with a further portion of calibration fat.
CAUTION — If there is fat on the septum it will contaminate the needle when the headspace gas is sampled and the contaminant may be transferred to the column; it is particularly important that such contamination be avoided when using capillary columns.